并行数据计算处理过程: 并行计算 Command Encoder
本章描述如何创建并使用 MTLComputeCommandEncoder 对象来编码并行数据计算状态和执行,然后提交它们并在设备上执行。
为了进行并行数据计算,参照如下主要步骤:
- 使用
MTLDevice的方法创建一个MTLComputePipelineState类型对象,它包含来自MTLFunction对象的编译好的着色程序代码,详见 Creating a Compute State.MTLFunction对象表示一个用 Metal 着色语言编写的着色程序。详见 Functions and Libraries. - 为
MTLComputeCommandEncoder对象设置MTLComputePipelineState对象,任一时刻,一个MTLComputeCommandEncoder只能被设置使用一个计算着色程序。详见 Specifying a Compute State and Resources for a Compute Command Encoder. - 为 state 对象设置资源 (
MTLBuffer,MTLTexture,MTLSamplerState) ,这些资源中包含了待处理数据或是被 state 对象返回的数据。详见 Specifying a Compute State and Resources for a Compute Command Encoder. 同时还要设置这些资源的参数索引表,这样 Metal 的框架代码才能为着色代码定位相关资源。在任一时刻,MTLComputeCommandEncoder可以关联多个资源对象。 - 按指定次数分发计算程序,详见 Executing a Compute Command.
创建一个并行计算管线 State
一个 MTLFunction 对象代表一段并行计算代码,它可以被一个 MTLComputePipelineState 对象执行。MTLComputeCommandEncoder 对象用于编码计算指令、设置入参、执行计算程序。创建 MTLComputePipelineState 对象是一种高开销的操作,因为它包含对并行计算着色程序的编译过程,所以可以选择适合 App 的 blocking 或者其他异步方法来完成这个工作。
- 同步创建
MTLComputePipelineState对象,可以调用下面两个MTLDevice对象的方法中的一个:newComputePipelineStateWithFunction:error:或者newComputePipelineStateWithFunction:options:reflection:error:。这些方法在 Metal 编译着色代码的时候阻塞当前线程。 - 异步创建
MTLComputePipelineState对象,可以调用下面两个MTLDevice对象的方法中的一个:newComputePipelineStateWithFunction:completionHandler:或者newComputePipelineStateWithFunction:options:completionHandler:。 这些方法立刻返回。Metal 异步编译着色代码来创建MTLComputePipelineState对象,创建完后调用completionHandler并且返回一个新的MTLComputePipelineState对象。
当创建 MTLComputePipelineState 对象的时候,也可以创建 reflection 数据(MTLComputePipelineReflection),它用于描述并行计算程序和它的入参的细节。 newComputePipelineStateWithFunction:options:reflection:error: 和 newComputePipelineStateWithFunction:options:completionHandler: 方法提供这个数据。如果不需要 reflection 数据,则不要创建它。更多关于如何分析 reflection 数据,详见 Determining Function Details at Runtime.
为并行计算 Command Encoder 指定 State 和资源
MTLComputeCommandEncoder 对象的 setComputePipelineState: 方法用于设定 Encoder 使用的 state 对象,包括编译好的并行计算着色程序,用于并行数据计算 pass。在任一时刻,一个 MTLComputeCommandEncoder 对象只能关联一个并行计算着色程序。
如下的 MTLComputeCommandEncoder 方法用于设定资源对象(缓存,纹理,采样器 state,线程组内存),这些资源对象是作为包含于 MTLComputePipelineState 对象的并行计算着色程序的入参来使用。
setBuffer:offset:atIndex:setBuffers:offsets:withRange:setTexture:atIndex:setTextures:withRange:setSamplerState:atIndex:setSamplerState:lodMinClamp:lodMaxClamp:atIndex:setSamplerStates:withRange:setSamplerStates:lodMinClamps:lodMaxClamps:withRange:setThreadgroupMemoryLength:atIndex:
每个方法都设置一个或多个资源给对应的并行计算着色程序入参,如图 6-1.
图 6-1 并行计算 Command Encoder 的参数列表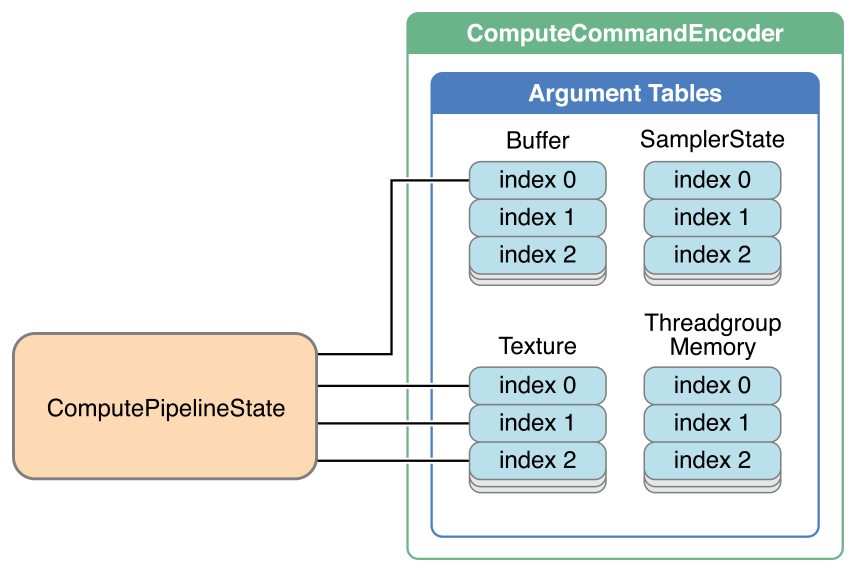
如上图所示,Encoder 对象中,缓存参数列表最多存放31个元素,纹理参数列表最多存放31个元素,采样器 state 参数列表最多存放16个元素。
线程组内存总量不能超过 16 KB,否则将导致错误。
执行并行计算指令
编码指令,来执行并行计算着色程序,可以调用 MTLComputeCommandEncoder 对象的 dispatchThreadgroups:threadsPerThreadgroup: 方法,并且设置线程组规模和线程组的数量。可以查询 MTLComputePipelineState 对象的 threadExecutionWidth 和 maxTotalThreadsPerThreadgroup 属性来优化在设备上执行的并行计算着色程序。
要使并行计算着色程序的执行最为高效,通过 dispatchThreadgroups:threadsPerThreadgroup: 方法指定的 threadsPerThreadgroup 参数应该是 threadExecutionWidth 的整数倍。一个线程组内的总线程数是入参 threadsPerThreadgroup 各分量的乘积,也就是 threadsPerThreadgroup.width * threadsPerThreadgroup.height * threadsPerThreadgroup.depth。 maxTotalThreadsPerThreadgroup 属性表示并行计算着色程序在设备上执行时,在一个线程组中允许的最大的线程数量。
并行计算程序按照 Encoder 被推入 command buffer 的次序执行。一个并行计算着色程序所拥有的所有线程组都执行完毕且计算结果都写入内存后,才表示这个并行计算着色程序执行完毕。这意味着前一个 Encoder 产生的数据可以被下一个 Encoder 使用。
要结束编码指令,调用 MTLComputeCommandEncoder 对象的 endEncoding 方法。对于同一个 command buffer 来说,在前一个 Encoder 结束编码后,才可以创建一个新的任意类型的 Encoder 来编码新的指令并推送之。
示例代码:执行并行数据计算着色程序
列表 6-1 展示了一个例子,创建并使用一个 MTLComputeCommandEncoder 对象对一个图形变换并行计算(这个例子没有展示 device, library, command queue,资源对象如何创建并初始化)。在例子中,先创建一个 command buffer,用它创建一个 MTLComputeCommandEncoder 对象,如何一个 MTLFunction 对象被创建出来表示来自于 MTLLibrary 对象中的着色程序 filter_main 的入口,着色程序在 列表 6-2 展示。接着 MTLFunction 对象被用来创建一个叫做 filterState 的 MTLComputePipelineState 对象。
示例代码的并行计算着色程序是要对一个图像进行变换和过滤操作,输入的是 inputImage,输出是 outputImage。首先调用 setTexture:atIndex: 和 setBuffer:offset:atIndex: 方法,为参数列表中的索引项设置了纹理和缓存对象。变量 paramsBuffer 指定了用于实施图像变换的值, inputTableData 指定了过滤权重。并行计算着色程序的线程组被设定为 2D,16 * 16。 dispatchThreadgroups:threadsPerThreadgroup: 方法将并行计算着色程序指令入队分派给线程待执行,然后 endEncoding 方法结束 Encoder 编码过程。最后 MTLCommandBuffer 对象的 commit 方法被调用,使得计算指令被尽快执行。
列表 6-1 在并行计算 state 上设置并运行程序
id <MTLDevice> device;
id <MTLLibrary> library;
id <MTLCommandQueue> commandQueue;
id <MTLTexture> inputImage;
id <MTLTexture> outputImage;
id <MTLTexture> inputTableData;
id <MTLBuffer> paramsBuffer;
// ... Create and initialize device, library, queue, resources
// Obtain a new command buffer
id <MTLCommandBuffer> commandBuffer = [commandQueue commandBuffer];
// Create a compute command encoder
id <MTLComputeCommandEncoder> computeCE = [commandBuffer computeCommandEncoder];
NSError *errors;
id <MTLFunction> func = [library newFunctionWithName:@"filter_main"];
id <MTLComputePipelineState> filterState
= [device newComputePipelineStateWithFunction:func error:&errors];
[computeCE setComputePipelineState:filterState];
[computeCE setTexture:inputImage atIndex:0];
[computeCE setTexture:outputImage atIndex:1];
[computeCE setTexture:inputTableData atIndex:2];
[computeCE setBuffer:paramsBuffer offset:0 atIndex:0];
MTLSize threadsPerGroup = {16, 16, 1};
MTLSize numThreadgroups = {inputImage.width/threadsPerGroup.width,
inputImage.height/threadsPerGroup.height, 1};
[computeCE dispatchThreadgroups:numThreadgroups
threadsPerThreadgroup:threadsPerGroup];
[computeCE endEncoding];
// Commit the command buffer
[commandBuffer commit];
列表 6-2 展示了先前示例相关的着色程序代码,它使用到的两个函数 read_and_transform 和 filter_table 没有展示。
列表 6-2 并行计算着色程序说明
kernel void filter_main(
texture2d<float,access::read> inputImage [[ texture(0) ]],
texture2d<float,access::write> outputImage [[ texture(1) ]],
uint2 gid [[ thread_position_in_grid ]],
texture2d<float,access::sample> table [[ texture(2) ]],
constant Parameters* params [[ buffer(0) ]]
)
{
float2 p0 = static_cast<float2>(gid);
float3x3 transform = params->transform;
float4 dims = params->dims;
float4 v0 = read_and_transform(inputImage, p0, transform);
float4 v1 = filter_table(v0,table, dims);
outputImage.write(v1,gid);
}